Archaeal Membranes Contain Which of the Following Lipids
They are generally called Thermophiles. Moreover thermophilic and extreme acidophilic Archaea possess membrane-spanning tetraether lipids that form a rigid monolayer membrane which is.
The isoprenoid components are ether linked to.
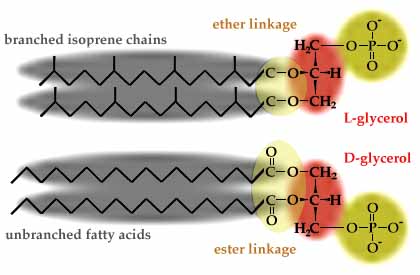
. In order to survive high temperatures their cell membrane membrane contains ether-linked lipids. The hydrophobic lipid tails are branched and fully saturated. Most organisms found in the Archaea are found in extreme enviroments such as very high temperatures.
In order to survive high temperatures their cell membrane membrane contains ether-linked lipids. It is composed of glycerol-ether lipids instead of glycerol-ester lipids. - Archaea have isopranyl glycerol ethers rather than fatty acid esters in their membrane lipids.
The branched chains of. Archaeal lipid tails consist of saturated isoprenoid hydrocarbon chains which are commonly 20 to 40 carbons long Sprott 2011. Glycerol diphytanyl diethers archaeol and glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraethers GDGTs 1.
However the phospholipids of archaebacteria are different from other bacteria in various ways. Which of the following is NOT a difference seen in archaeal membrane lipids relative to those of other organisms. The central carbon of the glycerol backbone has an S configuration.
Whereas the cell membranes of other bacteria is made up of straight chains without side branches or rings. These membranes are stable in concentrated 3-5 m NaCl solutions. They are generally calledThermophiles.
A backbone other than glycerol is used. - Archaea differ from bacteria in their tRNA composition ribosome. The hydrocarbon chains are attached via ether linkages instead of ester linkages.
Which of the following is NOT a difference of archaeal membrane lipids relative to those of other organisms. Most organisms found in the Archaea are found in extreme enviroments such as very high temperatures. The long hydrophobic tails are branched rather than being linear.
Archaeal membranes are mainly composed of two types of isoprenoid ether lipids. The membranes of extremely halophilic Archaea are characterized by the abundance of a diacidic phospholipid archaetidylglycerol methylphosphate PGP-Me which accounts for 50-80 mol of the polar lipids and by the absence of phospholipids with choline ethanolamine inositol and serine head groups. Also cell membranes of archaebacteria contain branched chain lipids.
Ether linkages instead of ester linkages are used. Fatty acid esters are replaced with long chain alcohol esters to the glycerol. In extreme environments mainly Archaea are encountered.
The archaeal cytoplasmic membrane contains unique ether lipids that cannot easily be degraded are temperature- and mechanically resistant and highly salt tolerant.
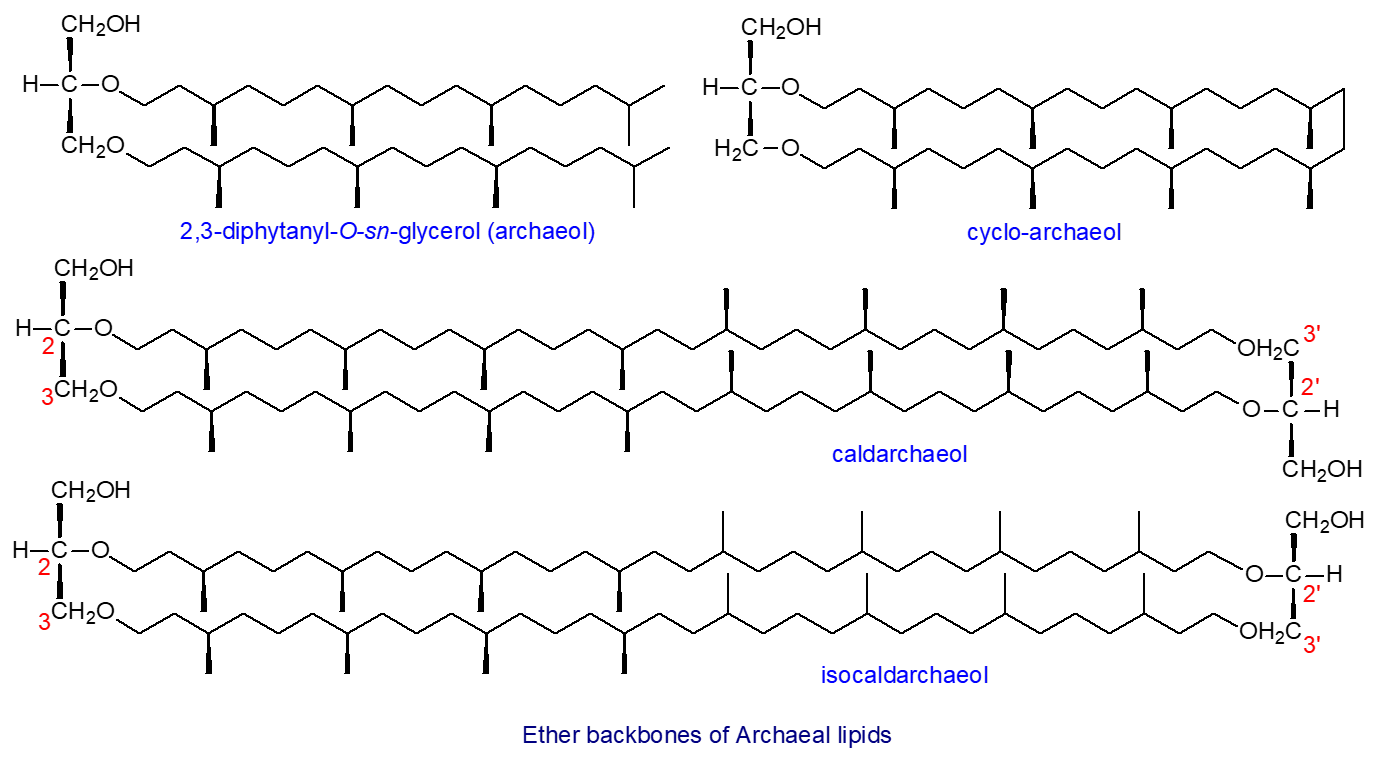
Di And Tetra Alkyl Ether Lipids Of The Archaea Archaeal Lipids
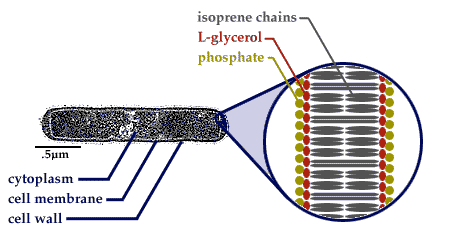
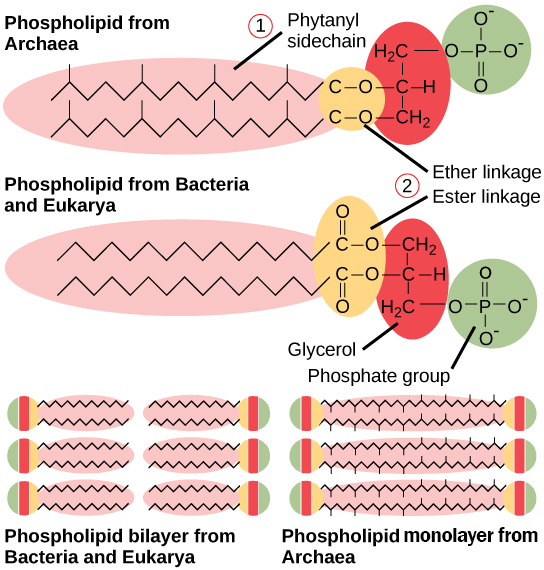
Comments
Post a Comment